Take 11 Minutes. Start Innovating with Design Thinking
This Articles Learning Goals:
💡Discover (Theory & Use Cases)
An introduction to the advantages the Design Thinking framework brings to a business, culture, and product.
🧭 Prepare (Leverage Framework)
Harness the Design Thinking process from brainstorming to testing. Prepare your approach to empower a team to focus on what’s important at every step of the design journey.
🔬 Try (Apply Techniques )
Explore methods and workshops to solve real-world problems.
How does design thinking help in innovation?
Design Thinking is as much a mindset as it is an approach to learning about users and translating insight into actionable solutions. As a framework, Design Thinking aims to help teams collaboratively and iteratively solve problems based on the user's needs rather than the whims of the creators (aka the business or design team).
Design Thinking can also enable you to set up the right team and approach product and service design from a more human lens. It is a helpful way to prioritize what’s most important to the user and design solutions that meet their deepest needs.
“Design thinking relies on the natural and coachable human ability to be intuitive, recognize patterns, and to construct ideas that are emotionally meaningful as well as functional.”
💡Discover Design Thinking
What is Design Thinking?
When we want to understand our users' needs better or wish to change their behaviour, a human-centred approach is the best way to identify, define, and solve a user’s challenge. Using empathy-based research, and speaking to actual users, will reveal important insight that will help your team build an optimal experience for those using your products and services. Further, solutions rooted in empathy often lead to happy, loyal users who become champions of your brand.
Design Thinking Use Case
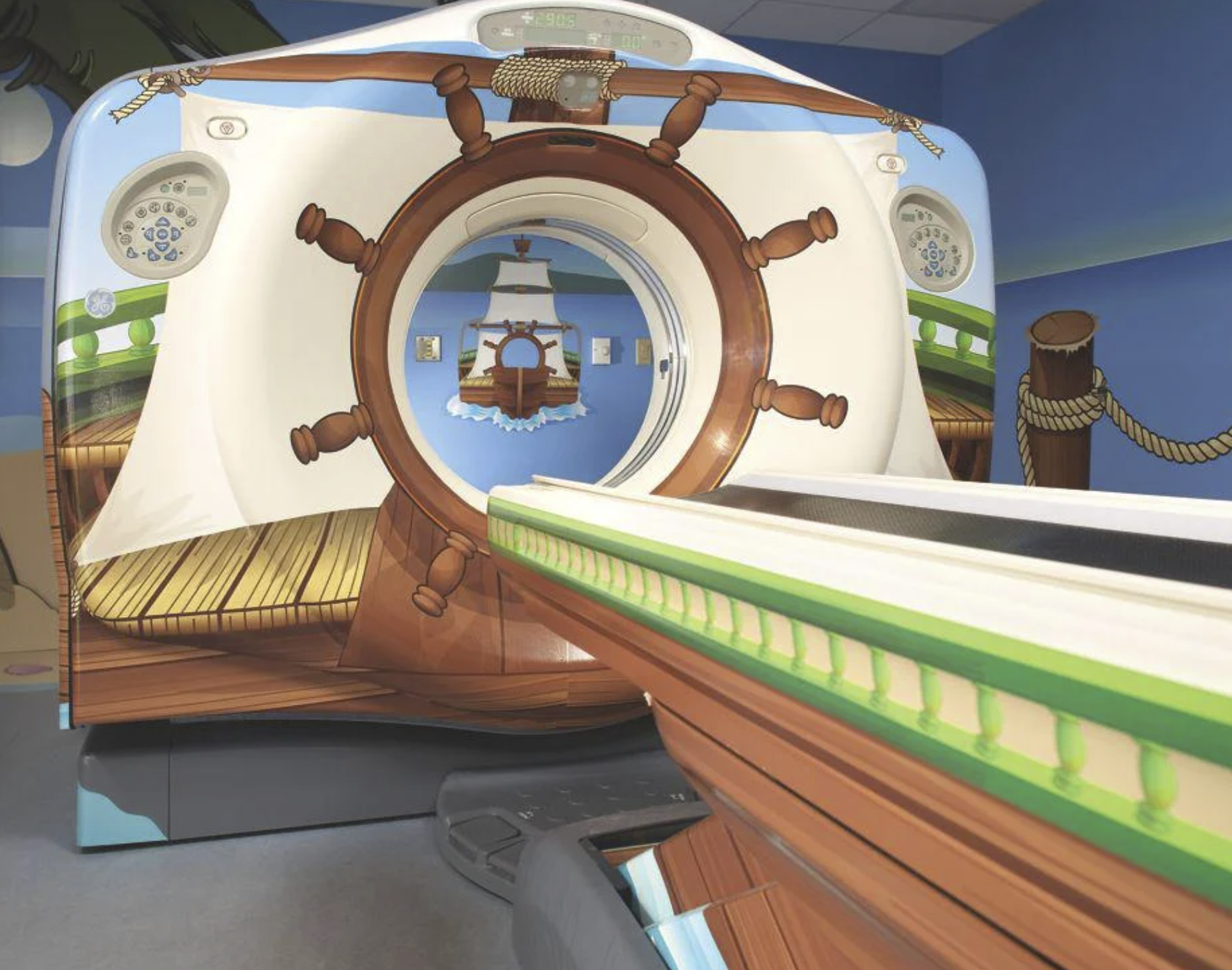
Transforming Young MRI Patient’s Experience: First, kids Were Terrified of Getting into MRIs. Then Someone Figured Out a Better Way!
Background
A Technologist for General Electric named Doug completed work on an enhanced MRI project. He went to see his creation in action at a children's hospital. However, he was surprised by his patients' fear of the scary machine he had designed.
Problem Framing
To Doug’s chagrin, he discovered, the kids’ feared his machine.
The hospitals sedate 80% of kids for MRI scans because they are terrified.
As a result of the fear, kids cannot remain motionless and ruin the scan results.
Processes to manage fear were causing resource issues.
If an anesthesiologist isn’t available, they reschedule the scan
As a result of schedule issues, kids and their families repeat the cycle of dread.
Solving the Problem
Instead of quitting or accepting the bad experience, he chose to see his product through the eyes of his user, a sick child, and he vowed to make a change. He would focus the next iteration of his product on user needs and rethink the experience.
Empathy for the users
He set out to observe and talk to various users and stakeholders involved in child development.
To build empathy and understand the young users he:
Observed children at a daycare centre.
Talked to child life specialists to understand the experience of pediatric patients.
Reached out to his network from GE, experts from a children’s museum, and medical professionals.
Build and test a prototype
GE’s Adventure Series redesigns MRIs with a pirate theme to make the procedures less scary for kids. Photo courtesy Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh of UPMC
Leveraging the insight collected from the empathizing and defining stages, his team ideated solutions and designed a prototype called the "Adventure Series" scanner. Finally, Doug’s team tested their innovative solution at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center's children's hospital.
Adventure Series prototype test:
Doug and his team transformed the MRI exam room into a kid's adventure story:
They plastered colourful decals on every surface in the room, excluding the machinery and electronics
They wrote an adventure script for the MRI medical team and parents to bring the adventure to life.
Then, the patient plays the lead role in the Adventure Series while receiving an MRI.
Results:
✔️ The number of patients requiring sedation decreased; and so
✔️ the need for anesthesiologists lessened; and
✔️ the number of scans/per day improved!
✔️ Best of all: Patient satisfaction increased by 90%,
Doug’s most rewarding moment was speaking to the mother whose six-year-old daughter had just completed an MRI, and the young girl tugged on her mother's skirt and asked, "Can we come back tomorrow, Mommy?".
Benefits of Design Thinking
Create features users want
When we empathize, we can better envision the future, strengthen user interactions, and prioritize the right features to support the vision.
Find out what matters most
Watch your users in action, in the places the challenges are occurring. Identify triggers and indicators that a product, service, or experience elicits an emotional response and seek to understand why or what is causing the reaction. Use their emotional reaction as a cue for an opportunity or solution in waiting.
Reduce risk to an organization
Embracing an iterative and human-centred approach reduces the risk of a project not meeting its objectives by uncovering the hidden needs of your users. In addition, Teams practicing Design Thinking are more synchronized and able to flag risks sooner and mitigate them.
Follow us on Instagram for simple tips on how to apply Design Thinking. Every day we share workshop ideas, practitioner tips, and design inspiration.
🧭 Prepare to Leverage Design Thinking
How to leverage the Design Thinking Framework
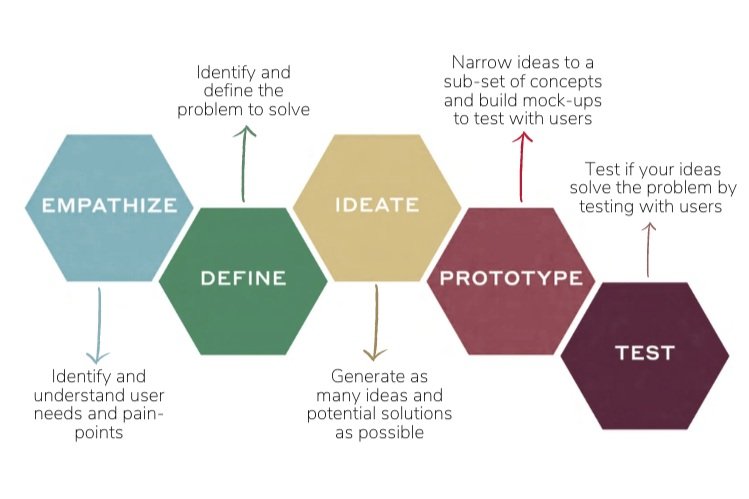
We love the world-renowned five-stage design thinking framework submitted by the Hasso Plattner Institute of Design at Stanford (the d.school).
framework credit: Hasso Plattner Institute of Design at Stanford (the d.school)
The 5-stages of Design Thinking are not linear because designing for real people means understanding complex behaviours which require non-sequential iterations. You can move through the 5-stages as your project requires of you. It’s never too early to test, and it's never too late to Empathize or redefine a need.
The 5 Stages, according to the d.school design thinking process:
Empathize: study your users' needs.
Define: articulate your users' needs and problems.
Ideate: question assumptions and assemble ideas.
Prototype: begin to create solutions.
Test: try your solutions out.
This framework is valuable for individuals, teams, and product and service design. Major corporations and non-profit organizations have developed competitive strategies to solve some of the world's most complex problems. It's also easy to facilitate and even easier to participate in. With the right mindset and a few tools in your toolkit, you and your team can start applying the framework.
Empathize
There should be no surprise that empathizing is the first step in the Design Thinking framework, as it allows up to put our users’ needs at the centre of a design.
Nurturing your human-centred design skills to uncover the needs of your users, partners, and stakeholders is what sets your solutions apart from the competition. By speaking with or observing your users' lives, you’ll begin to tell the story of why things aren’t working or why customer satisfaction is lower than expected.
Connect with Your Users
Understand empathy communication skills and get closer to your users so you can build better products, services, and teams.
Sympathy vs. Empathy
Sympathy is when you recognize someone else's pain or suffering. On the other hand, empathy is formed when we understand or share another person's feelings, desires, or motivations.
Try Empathy Mapping
An empathy map is a visual tool that helps us understand a user’s behaviour and attitude better. Start at the top and review and reflect on the prompts to get closer to your user.
Check out our blog on Empathy Mapping for simple step-by-step instructions and a free template.
Define
Leverages what you learn in the emphasize stage to translate insight into a defined problem statement or project’s vision. Often the trickiest of the 5 stages, the Define stage in Design Thinking, is all about diagnosing the right problem using the information a team gathers from their users and stakeholders. Further, the Define stage enables us to make meaning of what we’ve learned about our users to build a shared understanding of the problem or opportunity we want to address.
Try a Problem Funnel
State your problem in 40 words. Then, reduce it to 20 words. And then 10 words. Finally, 5 words.
Prioritizing needs and deciding where to allocate resources can be complex. The Design Thinking process is iterative and built to help leaders leverage what they have learned in other stages to build on their hypotheses and progress a project.
A simple way to practice defining the problem you are solving for your user with a Problem Funnel (example provided). If you can't keep things simple, you probably haven't gotten to the bottom of the problem yet.
Teams often miss the mark the first time they attempt the define stage, which is ok. A team will have many discoveries in the ideate, prototype, or test phase that will modify the problem statement or change it completely.
The good news is that the project has not launched or consumed many resources in the DEFINE phase. A leader should focus their team on learning valuable lessons that will help them make adjustments and reframe the problem.
Follow us on Instagram for simple tips on how to apply Design Thinking. Every day we share workshop ideas, practitioner tips, and design inspiration.
Ideate
Ideation is the third stage of Design Thinking and the least structured. Nevertheless, it is an exciting part of the process when imaginations can run wild.
Pro Tip: Go Big
The goal here is to arrive at many new ideas rather than to pick just one solution.
The focus here is on generating lots of ideas quickly and with few constraints and then working collaboratively to prioritize the solutions that hit the problem on the nose and drive the most impact.
Ideation Ignites Innovation
Get apparent solutions out of the team's head and steer beyond them.
Find surprising places and avenues for innovation.
How to start Ideating with your team?
When you start ideating, the goal is to generate as many ideas as possible (diverge) and then narrow them down (converge) into the most feasible and impactful ones that could lead the team towards a new or better product or service solution.
Design Thinking Check-in.
Empathize leads to user insights. Insights define the problem. Problem statements help teams ideate solutions concepts. A leader will consider revisiting a problem statement or plan for more user research if they learn something new or surprising in the Ideate stage.
Prototype
Prototypes are tangible representations of a solution that can help identify user needs before finishing the entire product.
Start a low-fidelity concept the team can test quickly with users, then move to high-fidelity ones. Always make time to get user feedback before iterating and rebuilding.
There are different prototype mediums you can use to tell your users’ stories and to validate their usefulness:
Low-fidelity prototypes use everyday items like paper, lego, and simple drawings.
Mid-fidelity prototypes use software or advanced drawing to demonstrate specific functionality like clickable areas on a mobile app.
High-fidelity prototypes are highly functional, interactive and close to the final product.
Testing and iterating as you move from low to high-fidelity prototypes is essential. You will save considerable resources by trying simple prototype ideas quickly with real people.
Pro Tip: Build low, mid, and high-fidelity prototypes in Canava for free. We highly recommend this tool, we used it to design our ebooks and all our templates.
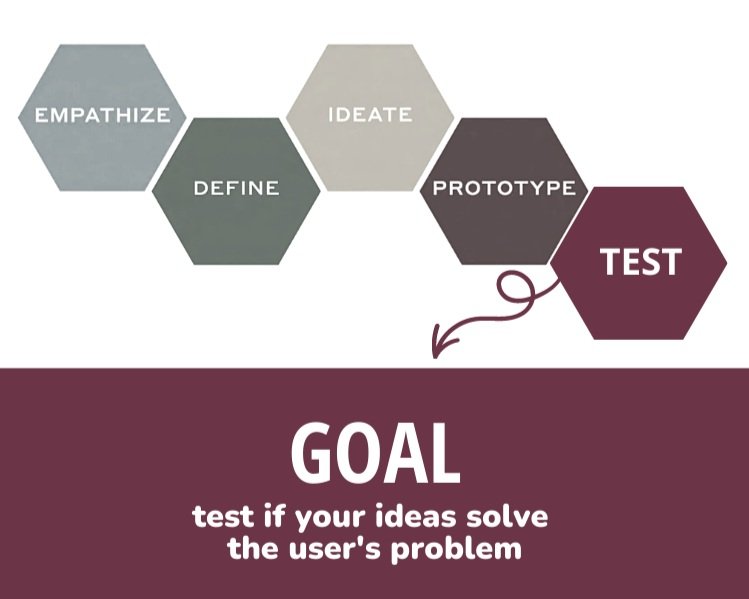
Test
Validate the prototype with your target users based on their feedback. To avoid bias, ensure you’re testing with real users and not your employees. Use the insights you gained in the IDEATE and PROTOTYPE phases to make improvements as necessary. Then repeat the process with a new prototype until you’ve got something that truly resonates with users.
How to Test Ideas
Start with a simple concept or prototype and build the solution in stages. Partner with your user to validate you are on the right path.
Design thinking's test stage frequently feeds into other stages:
Test findings enable the team to empathize with the users.
Tests may lead to insights that change how the problem statement is defined.
Tests may stimulate new ideas for solving the user problem.
Tests may help improve the prototype.
Collect user feedback quickly, and try TypeForm for free. Start learning your users' preferences with their simple feedback tool.
🔬 Try Design Thinking Methods
Try Human-centred Design
Human-centric design can help companies create better products, services, and user experiences. It combines insights into human behaviour with innovation methodology to drive creative thinking and generate actionable strategies based on user input.
Ways to try to leverage human-centred design:
Focus on your users' needs and comprehend the issue you're trying to solve, not instantly choose a solution.
Use the lens of the user to reveal solutions that are not initially obvious.
Challenge their assumptions to diagnose business challenges successfully.
Use their stakeholders to collect input and feedback to keep the project on track.
As a result, human-centred design principles are gaining greater prominence in today’s marketplace as companies strive to meet their customers’ evolving needs and ensure their continued success.
Explore Cross-functional Teams
Designing Thinking is not just for designers; everyone in an organization can benefit from taking a human-centric approach this their daily tasks.
When you empathize with your users, define the situation you're trying to innovate and develop a prototype, you want a cross-functional group of people doing it. So many hands and heads give you a wide range of perspectives, skills, and experiences, which leads to unique insights.
Everyone can learn to challenge their biases and assumptions to generate unique solutions to problems. Teams leveraging design thinking will harness their players' different perspectives and capabilities to work together faster.
Approach Design Thinking as a Non-linear Journey
Make it stand out
We love this philosophy - it’s one of designACE’s principals.
Try not to think of Design Thinking as a 1.2.3. step, rinse and repeat. Instead, the iterative disposition of design thinking is a collection of working methods you cycle through regularly.
We use the design thinking framework to tackle complex problems with many variables and moving parts. The design thinking approach lets you learn about your users, identify many solutions to the problem, and start trying those solutions. With each test, you will uncover more knowledge and discover things you then apply to refining your current solutions or developing a new one.
Practice empathy
Learn Empathy Mapping
Envisioning user perspectives and behaviours in an empathy map allows your team to align on an in-depth understanding of end users and make informed decisions about how to enhance their experience with your brand.
Empathy Mapping Learning Goals:
💡Discover (Theory & Framework)
Learn the Empathy Mapping framework and how businesses use it to drive results.
🧭 Prepare (Plan & Produce)
Plan an Empathy Mapping workshop.
🔬 Try (Template & Instructions)
Step-by-step instructions to try out Empathy Mapping with your team
Download our eBook: The Design Thinking Practitioners Guide
Equip yourself with tools to master design thinking and learn to use the resources to translate insight into a defined, actionable vision. In our Guides, you will master the process of applying design thinking to challenging problems and create a sustainable innovation pipeline for your organization.